Major telecoms firms are driving 5G initiatives in tele-diagnosis, remote surgeries and smart hospitals across China.
In Gaozhou, a city in China’s southwestern Guangdong province that is known for lychee, longan and banana farms, finding quality medical treatment has long been an issue because of the lack of talent and resources. But that situation has recently changed in this agricultural heartland, thanks to the latest advance in mobile communications: 5G.
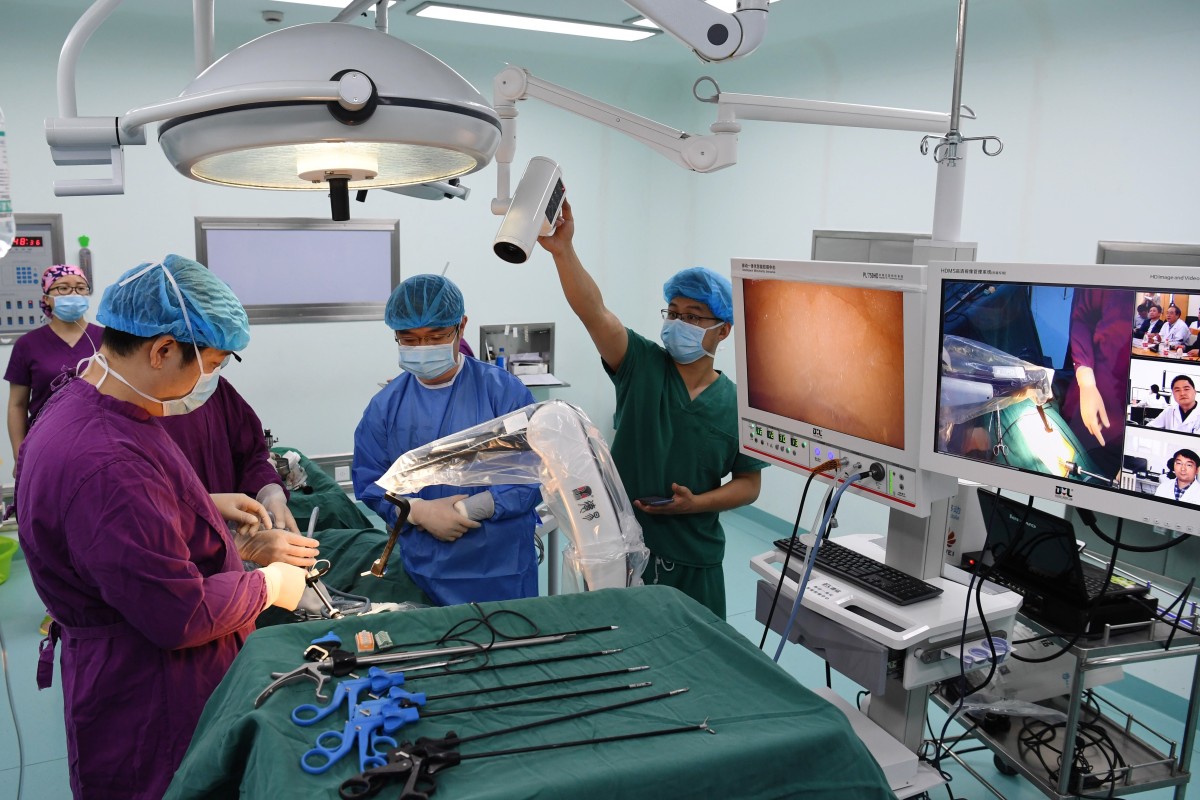
Surgeons at the People’s Hospital of Gaozhou got first-hand experience on how ultra-fast 5G connection works in April, when they performed an operation on a 41-year-old female patient whose congenital cardiac defect deteriorated to heart failure.
“Try to stay away from the triangle area mapped in 3D, or else stitches could cause myocardial damage,” said the Guangdong doctors, who watched the surgery live on a high-definition screen, while two other displays showed the patient’s dynamic ultrasonography and a three-dimensional rendering of her heart. The surgeons in Gaozhou had the same set of screens in their operating room.
In China, with a population of about 1.4 billion at the end of last year, the stakes are high for health care to become one of the major applications for 5G mobile technology because the world’s second biggest economy still must contend with an acute shortage of qualified doctors and nurses.
In the case of the surgical procedure in Gaozhou, the patient’s 600-megabyte ultrasonography file was transmitted in one second via the 5G-linked remote diagnostics platform, according to the Guangdong hospital’s estimate. By comparison, that file would have taken 20 minutes to send over a fixed-line broadband connection and three minutes via 4G.
The Guangdong provincial hospital is among a group of institutions that are working with telecommunications network operator China Mobile and infrastructure supplier Huawei Technologies to develop and test a range of applications with 5G ahead of its commercial roll-out on the Chinese mainland.
Their 5G collaboration is expected to support more initiatives in tele-diagnosis, remote surgeries and smart hospitals across China, where quality health care services common in urban areas are being made available in far-flung rural areas as well as for emergencies in which patients in critical condition cannot be moved to another location.
In March, China conducted its first remote surgery using robots with the support of a 5G network deployed by China Mobile and Huawei, according to state media.
The three-hour procedure on a patient suffering from Parkinson’s disease at the Chinese PLA General Hospital in Beijing was presided by a neurosurgeon, who was located 3,000 kilometres away in Sanya City on the southern province of Hainan. The surgeon implanted a neurostimulator, a device about the size of a traditional stopwatch, in the patient’s brain with the aid of robotic arms at the Beijing operating room that he remotely controlled via a 5G network-linked computer.
More 5G trials are expected to take place across the country, following the government’s granting of commercial 5G licences on June 6 to China Mobile, China Unicom, China Telecom and the China Broadcasting Network.
“The issuance of commercial licences will give telecoms network operators the impetus to step up their 5G deployment schedule,” said Wilson Chow, industry leader for technology, media and telecoms at PwC. He said China’s telecoms industry is expected to roll out consumer-driven 5G mobile applications by the end of this year.
With peak data rates up to 100 times faster than 4G, 5G networks will able to support the growing number of connected devices globally, including fitness-tracking watches, internet-linked televisions and smart speakers at home, as well as apps based on augmented and virtual reality technologies.
More importantly, 5G will serve as “the connective tissue” for the so-called Internet of Things, autonomous cars, smart cities and other new mobile applications – providing the backbone for the industrial internet, according to a Deloitte report. How 5G will impact the internet of things. While South Korea, Australia, the UK and the US have launched initial commercial 5G services in the second quarter, the scale of China’s market is likely to dwarf the combined size of those economies, negating any first-mover advantage.
Health care will increasingly become a priority area for 5G applications, as China deals with its ageing society, according to PwC’s Chow.
“5G can help ensure early diagnosis, early intervention and early treatment through applications that track user activity and other data,” he said. 5G applications that use virtual and augmented reality technologies can be applied to train professionals in health care and other fields, as well as in academic institutions, he added.